Complex wounds often involve exposed deep structures of the dermal layer, requiring prompt wound closure and tissue reconstruction. It is essential to quickly assess the defect and identify the most effective treatment method for optimizing the patient’s experience and outcome. Often, dermal substitutes are selected as a surgical option for temporizing the wound bed while also facilitating dermal repair with tissue generation.
Dermal substitutes are often used for patients who have sustained:
- Partial and full-thickness wounds
- Pressure ulcers, diabetic ulcers, venous ulcers, chronic ulcers, and vascular ulcers
- Surgical wounds (donor sites/grafts, post-Mohs surgery, post-laser surgery, podiatric, and wound dehiscence)
- Trauma wounds (abrasions, lacerations, second-degree burns, and skin tears)
- Draining wounds
NovoSorb BTM (Biodegradable Temporizing Matrix) is used by clinicians across a range of specialties, including those who perform plastic, burn, reconstructive, trauma, and general surgery. Here are some of the main benefits of using NovoSorb BTM.
1. Successful Temporizing Method for Wound Closure
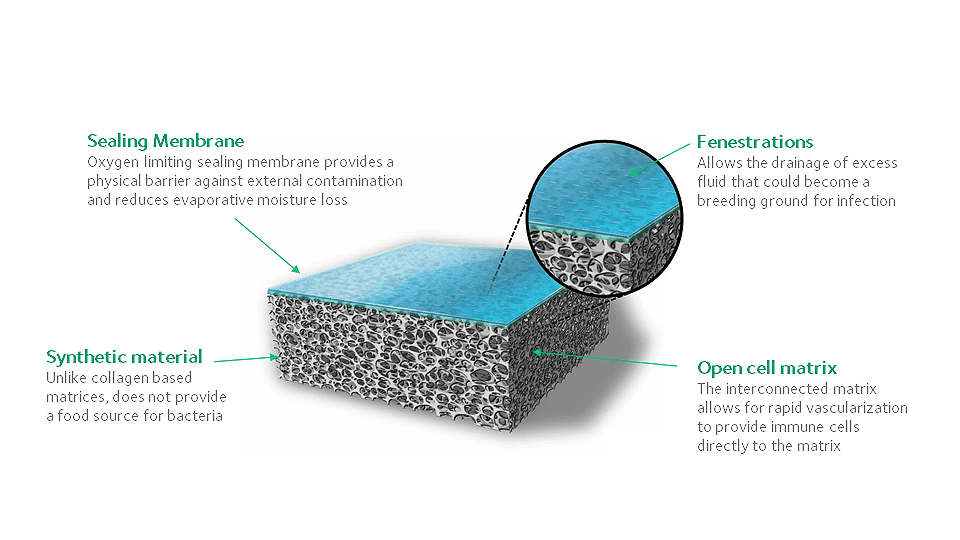
Exposed wounds may be susceptible to external contamination and uncontrolled evaporative fluid loss, which may jeopardize the body’s thermoregulation. NovoSorb BTM’s bilayer structure consists of two layers, a temporary sealing membrane on top and a bioabsorbable open-cell matrix beneath. When NovoSorb BTM is applied to the wound bed, the transparent sealing membrane physiologically seals the wound,[1] providing a barrier against external bacteria and helping to reduce evaporative moisture loss.
Without the use of a temporizing measure such as NovoSorb BTM, surgeons are often dependent upon donor site availability in cases requiring primary skin grafts for wound closure. NovoSorb BTM gives surgeons control over the treatment process, as the sealing membrane can be removed at their discretion when the matrix undergoes full cellular integration—allowing for staged treatments and management of medical issues before definitive wound closure.
2. Synthetic Dermal Matrix for Wound Reconstruction
Various dermal templates, including those of biological and synthetic origin, have been developed and clinically adopted for treating skin trauma and reconstructing skin defects. NovoSorb BTM is the world’s first 100% synthetic dermal matrix and does not contain any biological material. Consisting of medical-grade biocompatible polymers, NovoSorb BTM is designed to facilitate tissue growth and be resorbed over time as the wound continues to remodel.
NovoSorb BTM’s proprietary technology allows this novel device to maintain its product integrity and robustness. Read on to learn about the impact of NovoSorb BTM’s synthetic composition in the presence of infection.
3. Robust in the Presence of Infection
Bacteria-related infections are an ever-present threat with traumatic wounds. Fortunately, NovoSorb BTM is clinically shown to be robust in the presence of infection,[2] due in part to its synthetic material. NovoSorb BTM’s polymer composition does not contain biological components that would serve as a food source for bacteria to feed upon, often allowing an infection to be treated with NovoSorb BTM remaining in place. Should an infection occur, NovoSorb BTM’s transparent sealing membrane allows for simple observation and consists of fenestrations where the underlying turbid pus or discharge may be expressed for culturing, with local and/or systemic management of the infection according to standard of care.
4. Minimized Scarring & Contracture
The body’s natural wound repair process is chaotic, laying down fibrotic tissue to rapidly close the wound. This reparative healing response often results in the overproduction of tissue, causing scarring or contracture. NovoSorb BTM provides a matrix to organize the wound into a series of interconnected microwounds, which the body can heal in an organized regenerative manner. NovoSorb BTM’s microarchitecture is designed to minimize scarring and contracture for improved functional and cosmetic outcomes.[3]
Early mobilization is also critical in preventing scarring and contracture and supporting the patient’s return to function. Surgeons must always identify when patient mobilization can safely begin without affecting the dermal substitute’s integrity.
5. Zero Prep or Tissue Tracking
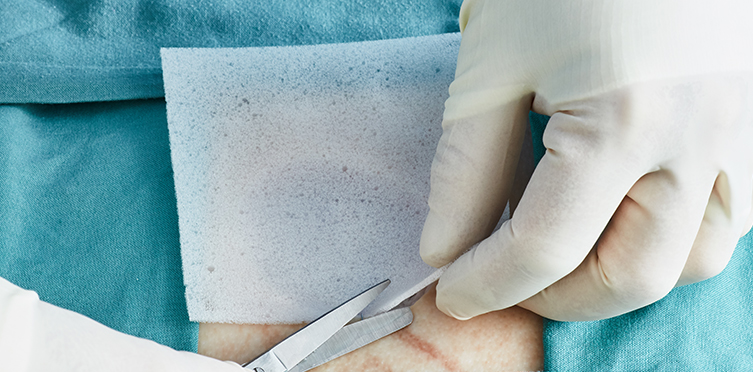
Because NovoSorb BTM does not contain biological material or sensitizing proteins, it does not require preparation, cold storage, or tissue tracking, which offers the surgeon and hospital great potential to save on OR time and resources. The surgeon simply trims NovoSorb BTM to the wound edges and secures it with staples or sutures. There is no need for rinsing, reconstituting by soaking, or other pre-treatments.
- No tissue tracking – no biological components
- No cold storage – can be stored at room temperature
- Easy application – cut and apply with sutures or staples
6. Lower Cost
Most temporizing dermal substitutes contain derivatives of biological origin, often requiring serial application, as the product’s integrity may be quickly compromised. Serial application is likely to increase the total episodic cost of care and impact the patient experience throughout the healing process. The time and effort saved by using NovoSorb BTM’s synthetic dermal template may be substantial.
7. Successful Outcomes
Excellent clinical outcomes across a range of indications, surgical specialties, and anatomical locations have been reported for NovoSorb BTM. NovoSorb BTM has shown to be effective in the following complex wounds:
- Exposed bone, tendon, or deep structures
- Large wounds
- Severe bacterial infections such as necrotizing fasciitis or meningococcal septicemia[6]
- Pediatric reconstruction
NovoSorb BTM promotes the growth of a neodermis, aiding in limb salvage[4]
With NovoSorb BTM, surgeons can graft when ready, in stages, or all at once[5]
NovoSorb BTM is clinically shown to be robust in the presence of infection, maintaining product integrity [2]
NovoSorb BTM can successfully help the body manage soft tissue injuries in the pediatric population[7]
If you are a clinician exploring options for treating severe skin trauma, be sure to consider NovoSorb BTM. To learn how NovoSorb BTM can provide long-lasting successful outcomes and other substantial benefits for both patients and physicians, reach out to our team of experts today at (302) 268-6163.
Note: this document contains general guidelines and is not designed to replace existing institutional protocols or professional clinical judgment regarding patient care. Please refer to the instructions for use.
______________
[1] Dearman BL, Li A, Greenwood JE. Optimization of a polyurethane dermal matrix and experience with a polymer-based cultured composite skin. Journal of Burn Care & Research. 2014; 35(5): 437-48.
[2] Greenwood JE, Dearman BL. Comparison of a sealed, polymer foam biodegradable temporizing matrix against Integra® dermal regeneration template in a porcine wound model. Journal of Burn Care & Research. 2012; 33(1):163-73.
[3] Solanki NS, York B, Gao Y, Baker P, Wong She RB. A consecutive case series of defects reconstructed using NovoSorb® Biodegradable Temporising Matrix: Initial experience and early results. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery. 2020; 73(10):1845–53.
[4] Partain KP, Noffsinger D, Thakkar RK, Fabia R. Pediatric limb salvage after severe thermal injury. Burns Open. 2020; 4(2):78–80.
[5] Greenwood JE, Schmitt BJ, Wagstaff MJD. Experience with a synthetic bilayer Biodegradable Temporizing Matrix in significant burn injury. Burns Open. 2018;2(1):17-34.
[6] Wagstaff MJD, Caplash Y, Greenwood JE. Reconstruction of an anterior cervical necrotizing fasciitis defect using a biodegradable polyurethane dermal substitute. Eplasty. 2017; 17:29–36.
[7] Crowley K, Balaji S, Stalewski H, Carroll D, Mariyappa-Rathnamma B. Use of Biodegradable Temporizing Matrix (BTM) in large trauma induced soft tissue injury: A two stage repair. J Pediatric Surgery; 2020.


