SUPRATHEL®


PolyNovo is pleased to announce the acquisition of exclusive sales and distribution rights for SUPRATHEL® in the U.K., Australia, and New Zealand. SUPRATHEL® is manufactured by PolyMedics (PMI) and is backed by a large body of clinical evidence from around the world with over 240,000 patients treated to date.
SUPRATHEL® is an innovative skin substitute indicated for the treatment of epidermal and dermal wounds, such as partial thickness burns and split thicknes skin graft (STSG) donor sites.

Just like a second skin, SUPRATHEL® covers the wound and leads it through a quick, complication free healing process.
SUPRATHEL® was designed to share the same barrier properties as human skin, including elasticity, permeability to water vapour, and impermeability to bacteria.
Simple. Effective. Reliable.
- Single application – stays on wound until re-epithelialisation is complete
- Contours and adheres to wound bed
- Significant pain relief 1–3
- Low infection rates 2, 11
- Reduced treatment costs 2, 4-5
- Excellent cosmetic outcomes and scar quality 6,7
- Reduced inflammatory reaction 8,9
- Reduced grafting rates 10
Indications
- Partial thickness burns
- Partial thickness burns with areas of full thickness
- STSG donor sites
- Chronic wounds
- Abrasions
Case Study
Description
-
Age of patient 53
-
Indication Partial thickness burn
-
Gender Male
-
Therapy SUPRATHEL ®
-
Aetiology Electrical burn, right hand
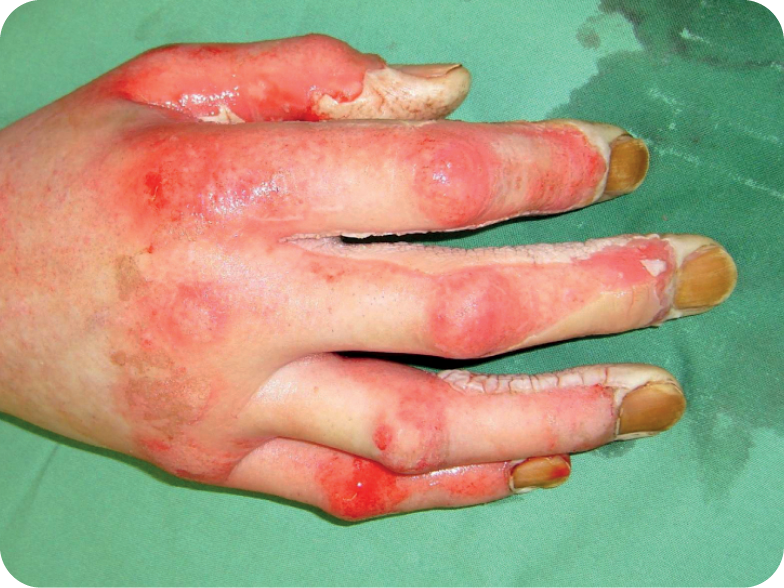 Day 1, debridement
Day 1, debridement
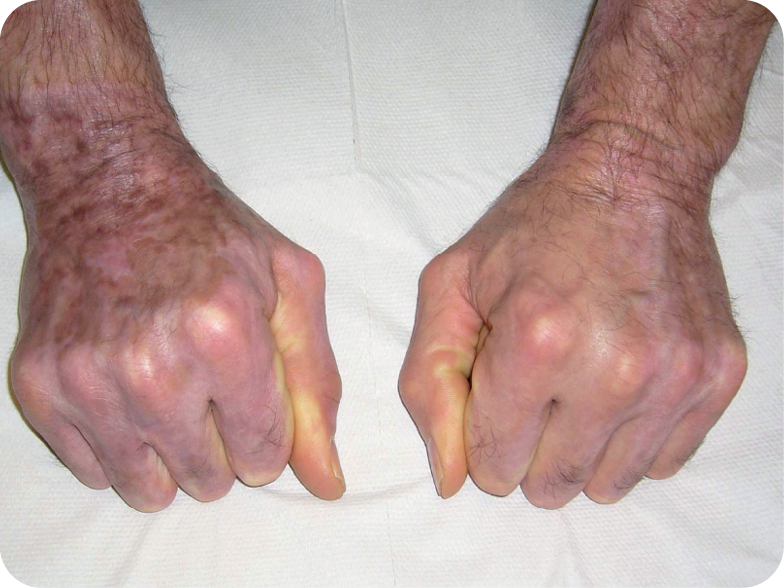 8 months after presentation
8 months after presentation
-
Hospital for Trauma Surgery Burn Center, Marienhospital Stuttgart/Germany
-
Dr. med. Christian Uhlig
Want more information about SUPRATHEL®?
Get in touch with PolyNovo representative
For full device details, including indications, contraindications, warnings and precautions, refer to the Instructions for Use.
The information on this page is intended for education purposes only and exclusively aimed at health care professionals.
Always read the label and follow the instructions for use including the contraindications, warnings, and precautions.
References
- Uhlig et al. 2007: Burns. 33(2): 221-9
- Schwarze et al. 2008: Ann Plast Surg: 60(2): 181-5
- Schwarze et al. 2007: Burns: 33(7): 850-4
- Everett et al. 2015: J Wound Care 24(7):S4-8
- Glat et al. 2014: Abstract, 46th Annual Meeting of the ABA
- Kaartinen and Kuokkanen 2011: J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 45(4-5): 200-3
- Keck et al. 2012: Burns 38(3): 388-95
- Gürünlüoglu et al. 2019: J Burn Care Res, in press
- Demircan and Gürünlüoglu 2019: Abstract, 51st Annual Meeting of the ABA
- Schriek et al. 2022: Eur Burn J: 3, 1-9
- Hundeshagen et al. 2018: J Burn Care Res Feb 20;39(2) 261-267


